Marfan Syndrome Fibrillin 1
Marfan syndrome fibrillin 1. Here we review the consequences of engineered Marfan syndrome mutations in fibrillin-1 at the protein cellular and organismal levels. Contractural arachnodactyly is due to mutations in FBN2. Here we review the consequences of engineered Marfan syndrome mutations in fibrillin-1 at the protein cellular and organismal levels.
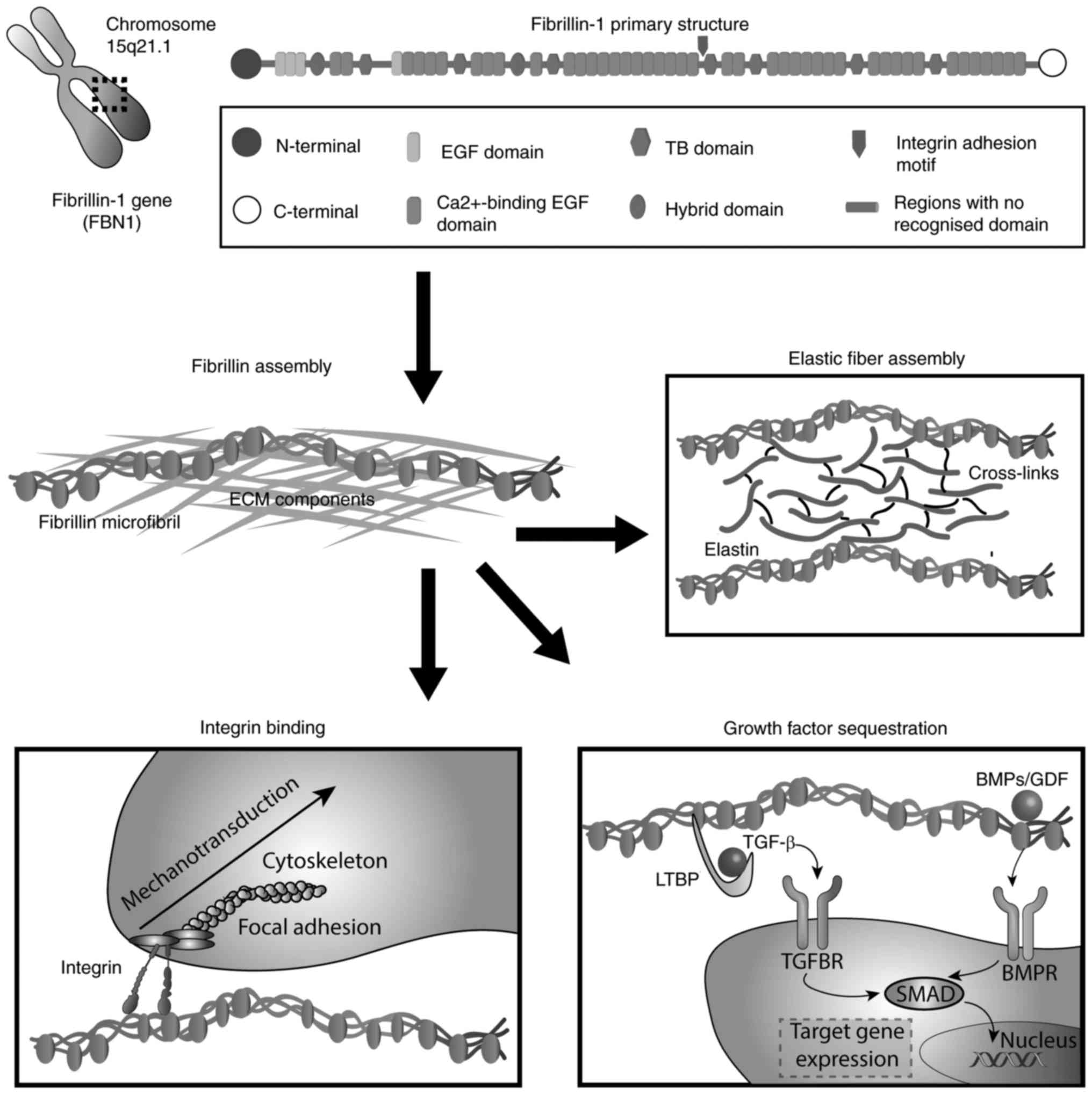
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal-dominant connective-tissue disorder usually caused by mutations in the gene that encodes fibrillin-1 Fibrillin-1 is the major constituent of extracellular. A number of conditions related to Marfan syndrome are also due to FBN1 mutations. The signs and symptoms of Marfan syndrome vary widely in severity timing of onset and rate of progression.
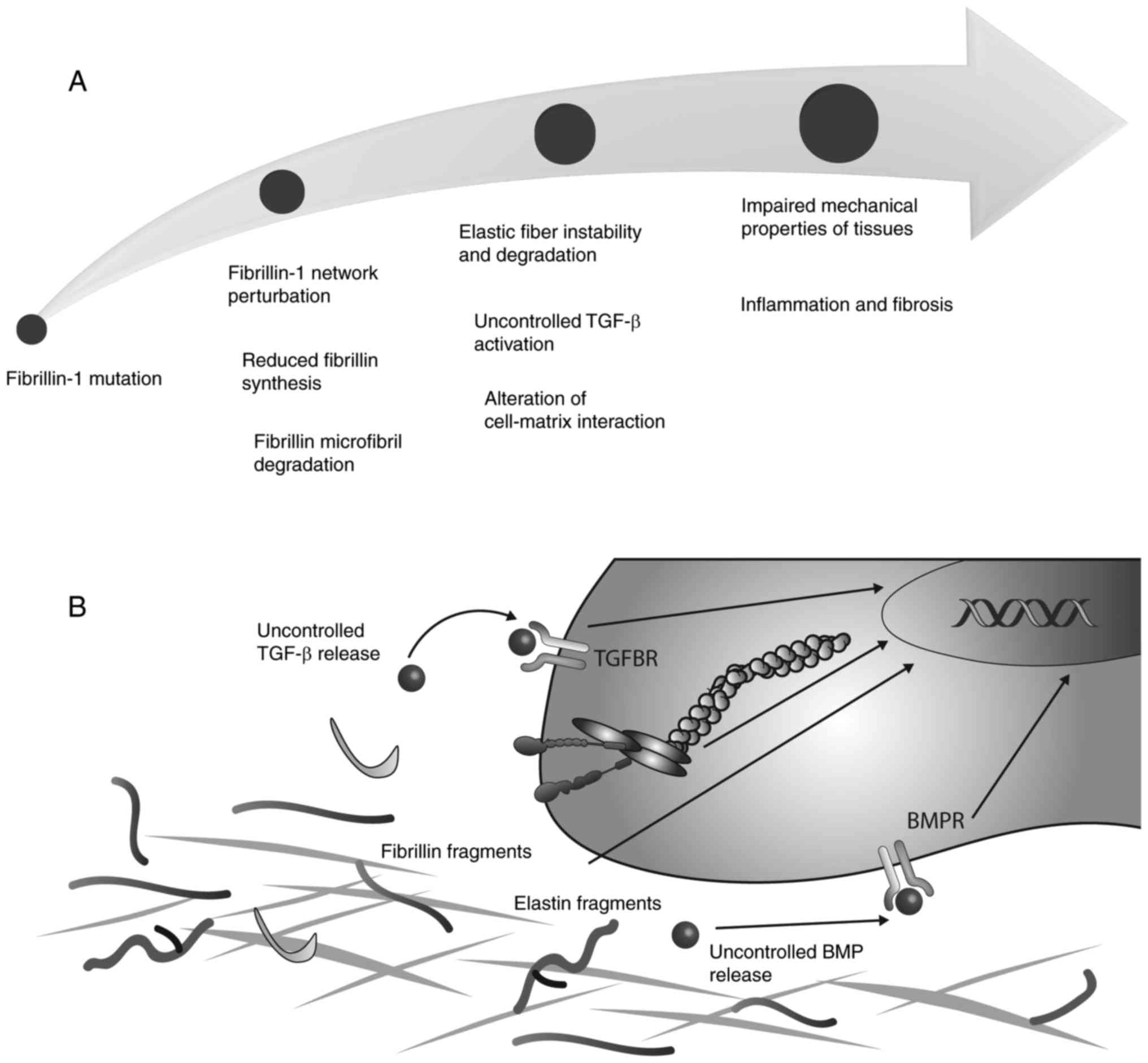
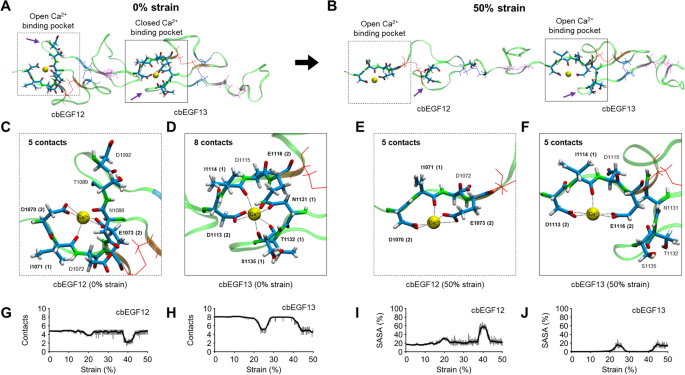
These mutations lead to a severe reduction in the amount of fibrillin-1 available to form microfibrils. Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene give rise to Marfan syndrome a connective tissue disorder with clinical complications in the cardiovascular skeletal ocular and other organ systems. Marfan syndrome is a genetic condition caused by a mutation or change in one of your genes called the fibrillin-1 FBN1 geneThe FBN1 gene makes fibrillin-1 which is a protein that forms elastic fibers within connective tissue.
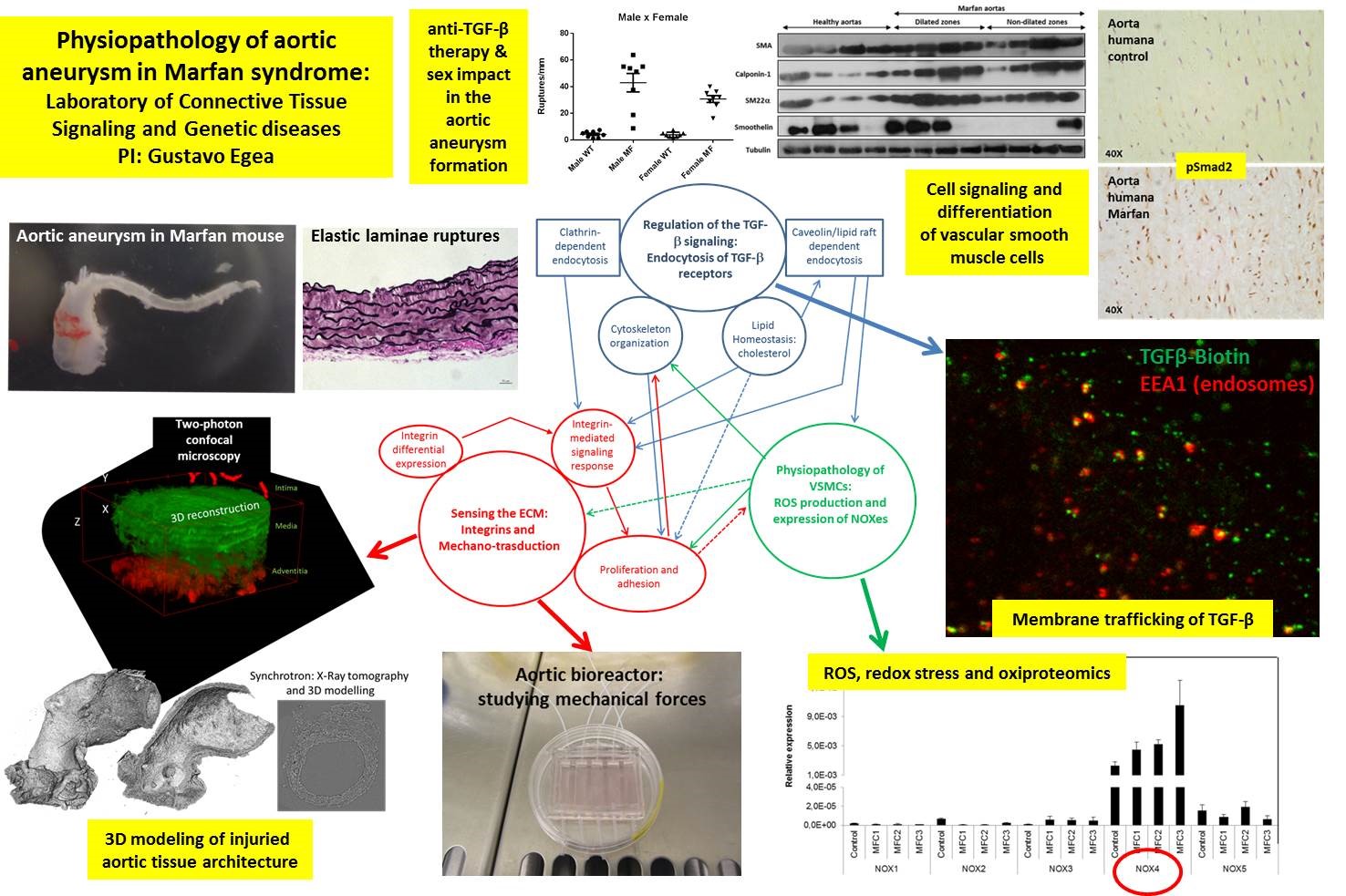
Marfan syndrome is a disorder that affects the connective tissue in many parts of the body. Mutations to the fibrillin-1 gene FBN1 are responsible for Marfan syndrome which manifests clinically via ocular musculoskeletal and cardiovascular disorders the most devastating of which is aortic root dilatation dissection and rupture. Most people who have Marfan syndrome inherit it from their parents.
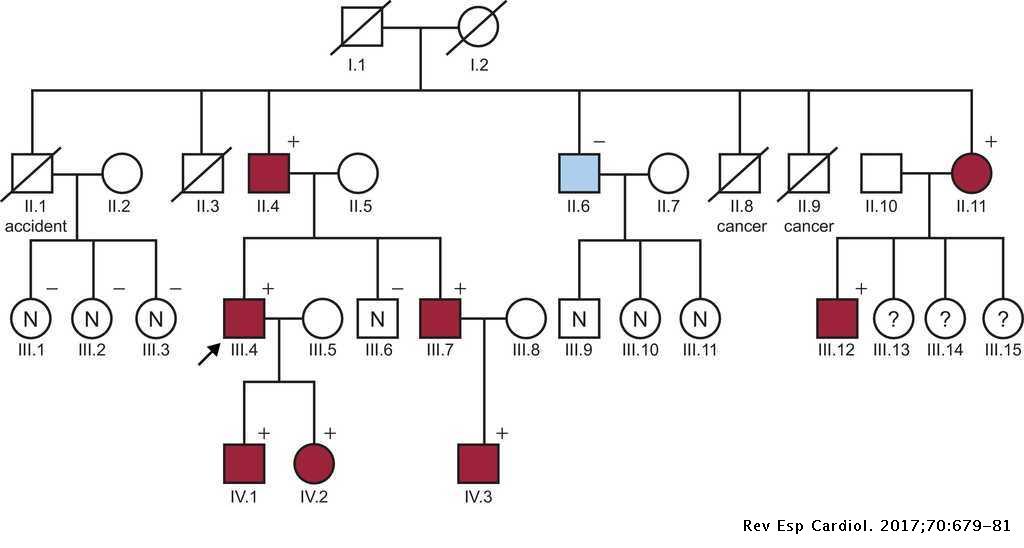
Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene give rise to Marfan syndrome a connective tissue disorder with clinical complications in the cardiovascular skeletal ocular and other organ systems. To our knowledge this sequence variant has been reported as a polymorphism rs113602180 but it is the first report identifying it as the genetic cause of Marfan syndrome. Mutations in FBN1 produce Marfan syndrome a pleiotropic autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder with prominent manifestations in the skeleton eye and cardiovascular system.
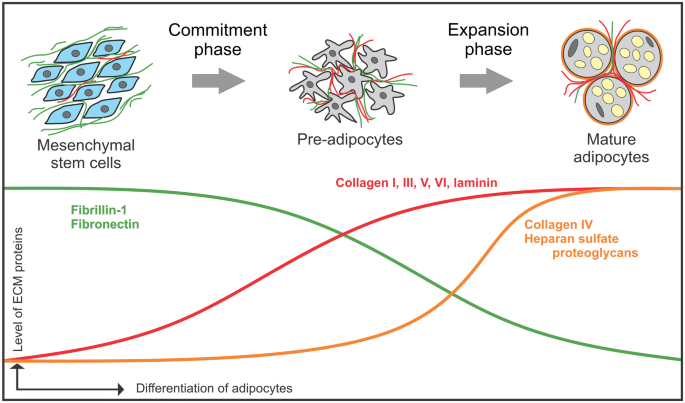
This means that fibrillin-1 mutations were notfound in 72 more than two thirds of the Marfans studied. Fibrillin-1 is essential for the proper formation of the extracellular matrix including the biogenesis and maintenance of elastic fibers. Fibrillin-1 also affects levels of another protein that helps control how you grow.
Marfan syndrome MFS is an inherited systemic disorder of the connective tissue caused by mutations in the fibrillin-1 FBN1 gene. Marfan syndrome also called Marfans syndrome is a genetic disorder primarily caused by mutations in the FBN1 fibrillin-1 gene.
Arakelyan published Fibrillin-1 and Marfan syndrome Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
Here we review the consequences of engineered Marfan syndrome mutations in fibrillin-1 at the protein cellular and organismal levels. Marfan syndrome is a genetic condition caused by a mutation or change in one of your genes called the fibrillin-1 FBN1 geneThe FBN1 gene makes fibrillin-1 which is a protein that forms elastic fibers within connective tissue. PDF On Oct 30 2017 Hayk S. To our knowledge this sequence variant has been reported as a polymorphism rs113602180 but it is the first report identifying it as the genetic cause of Marfan syndrome. Marfan syndrome also called Marfans syndrome is a genetic disorder primarily caused by mutations in the FBN1 fibrillin-1 gene. Marfan syndrome is typically an autosomal dominant disorder meaning that people who inherit only one copy of the Marfan FBN1 gene from either parent will develop Marfan syndrome and transmit it to their children. MFS shows autosomal dominant transmission and an estimated incidence of 1 in 5000 live births. Marfan syndrome MFS is an inherited systemic disorder of the connective tissue caused by mutations in the fibrillin-1 FBN1 gene. Arakelyan published Fibrillin-1 and Marfan syndrome Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
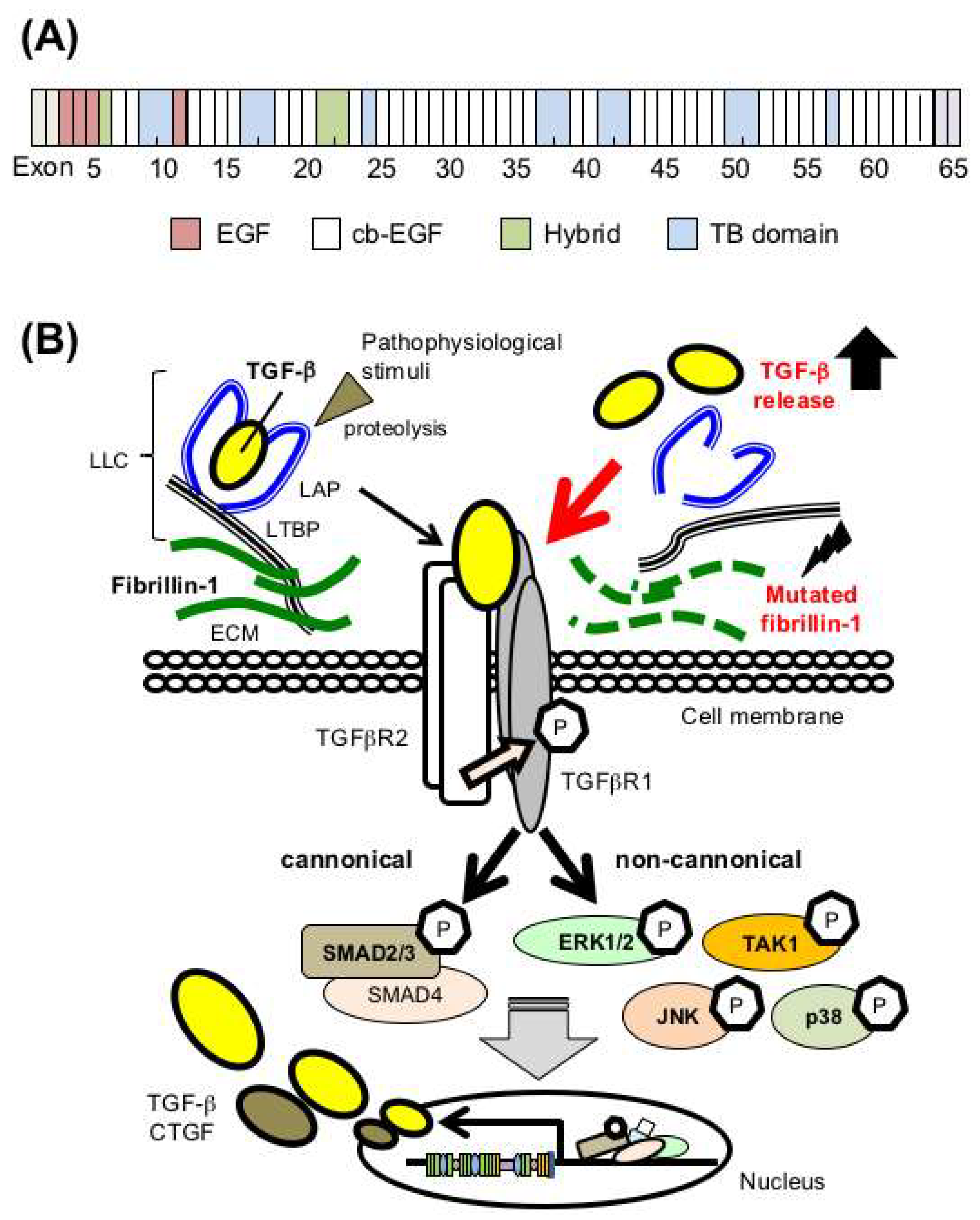
Marfan syndrome is a disorder that affects the connective tissue in many parts of the body. 94 filas Marfan syndrome affects most organs and tissues especially the skeleton. Mutations to the fibrillin-1 gene FBN1 are responsible for Marfan syndrome which manifests clinically via ocular musculoskeletal and cardiovascular disorders the most devastating of which is aortic root dilatation dissection and rupture. These mutations lead to a severe reduction in the amount of fibrillin-1 available to form microfibrils. FBN1 gene mutations that cause Marfan syndrome reduce the amount of fibrillin-1 produced by the cell alter the structure or stability of fibrillin-1 or impair the transport of fibrillin-1 out of the cell. Marfan syndrome is caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene on chromosome 15 which encodes fibrillin 1 a glycoprotein component of the extracellular matrix. Marfan syndrome MFS is a connective tissue disorder caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene NM_0001384 encoding the fibrillin-1 protein1 Patients with MFS often have aortic dilation requiring aortic surgery to prevent aortic dissection2 However phenotypic expression and age at manifestations onset are known to vary widely in patients with MFS3 Over 2900 different FBN1.

























Post a Comment for "Marfan Syndrome Fibrillin 1"