Pathophysiology Of Parkinson Disease
Pathophysiology of parkinson disease. The characteristic tremors associated with Parkinsons disease are an example of this. Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells or neurons in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired andor die. It affects approximately 15 to 20 of the elderly population over 60 years and 4 for those over 80 years of age.
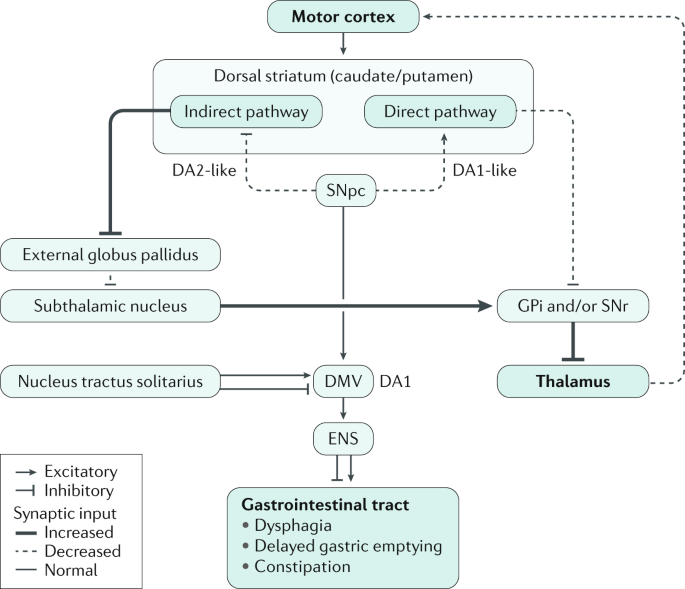
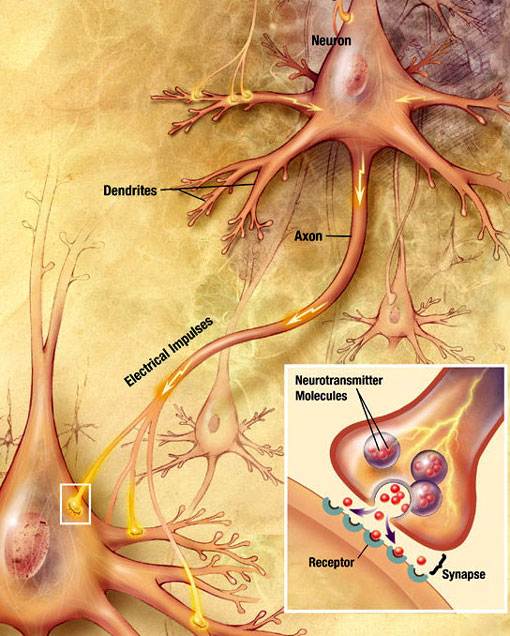
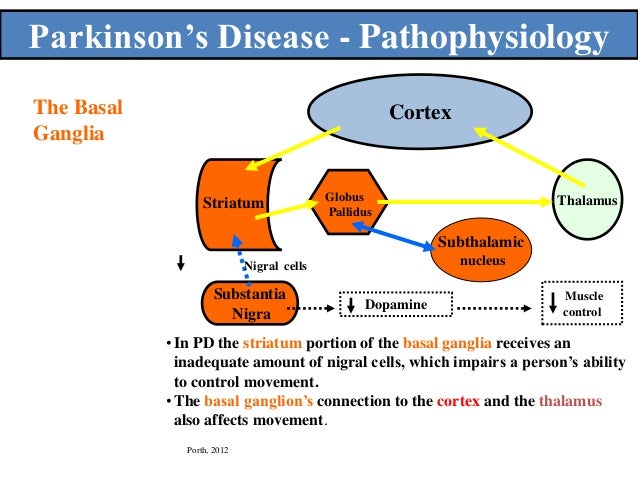
Considering that there are no laboratory tests biomarkers or imaging studies to confirm the disease the diagnosis of PD. These neurons are interconnected and they communicate with each other through release of some chemicals called neurotransmitters. Parkinsons disease is a progressive disease with selective dopaminergic neuronal loss.
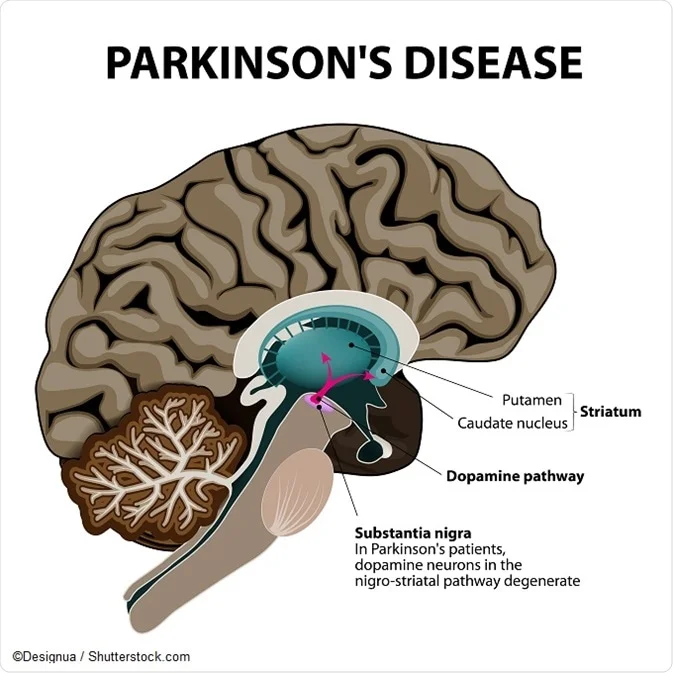
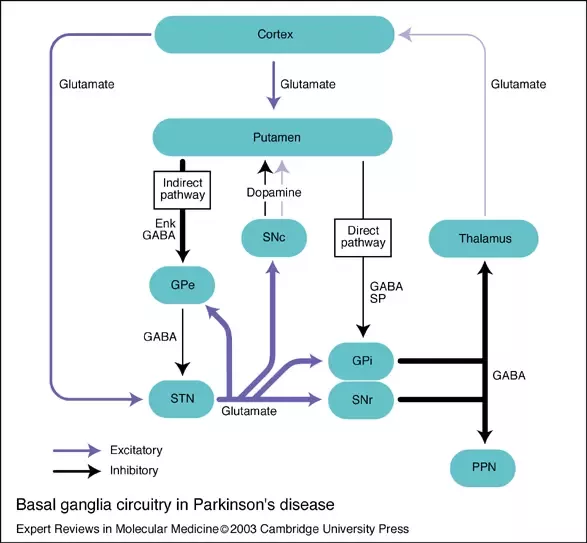
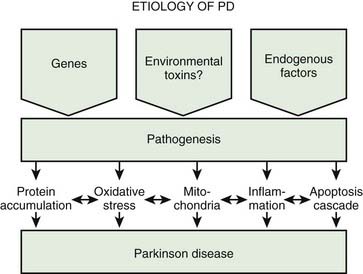
This book about Parkinsons disease provides a detailed account of etiology and pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease a complicated neurological condition. Dopamine depletion in the striatum is the hallmark of PD and of its animal models still. Environmental and genetic factors involved in the causation of Parkinsons disease have been discussed in detail.
Parkinsons disease PD is characterized by motor and nonmotor cognitive and limbic deficits. The symptoms usually emerge slowly and as the disease worsens non-motor symptoms become more common. 1 Parkinsons Disease Jerrold Burroughs Chamberlain College of Nursing Pathophysiology Prof.
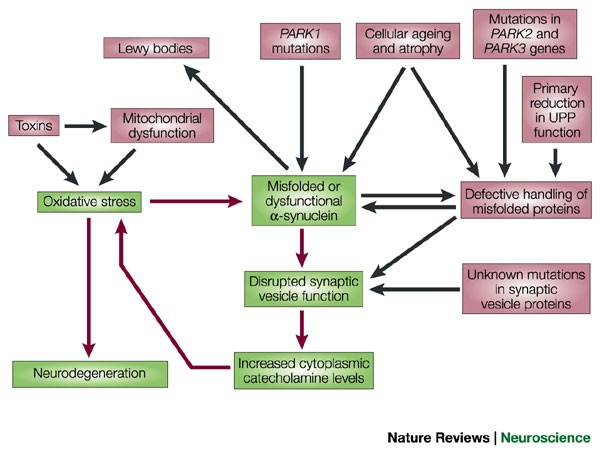
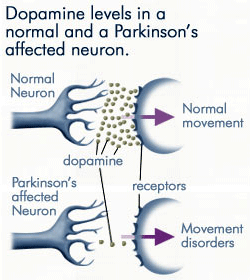
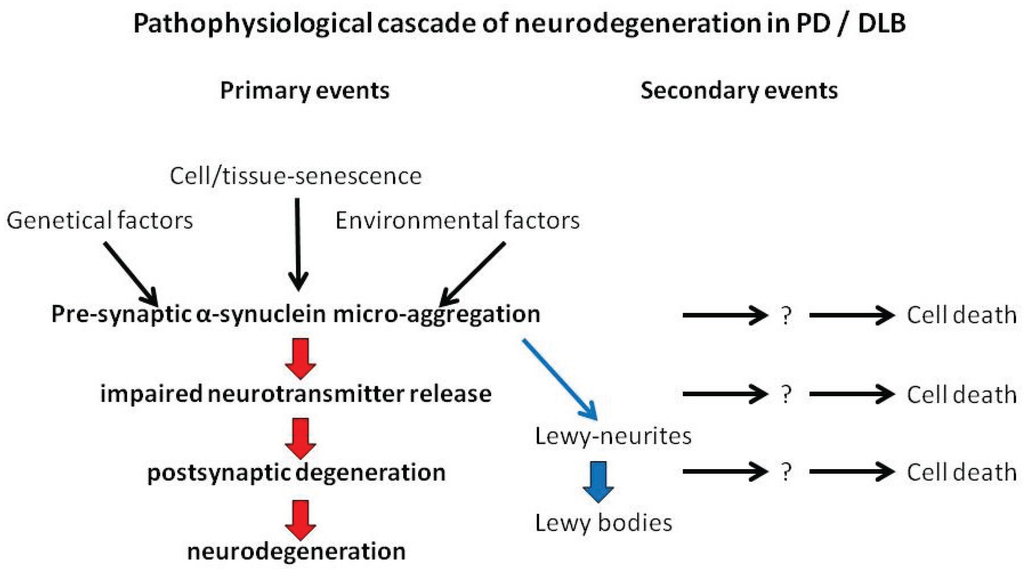
Normally these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. Scientists have also determined that one of the cellular mechanisms that are associated with Parkinsons disease is an accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein. When the neurons die or become impaired they produce less dopamine which causes the movement problems of Parkinsons.
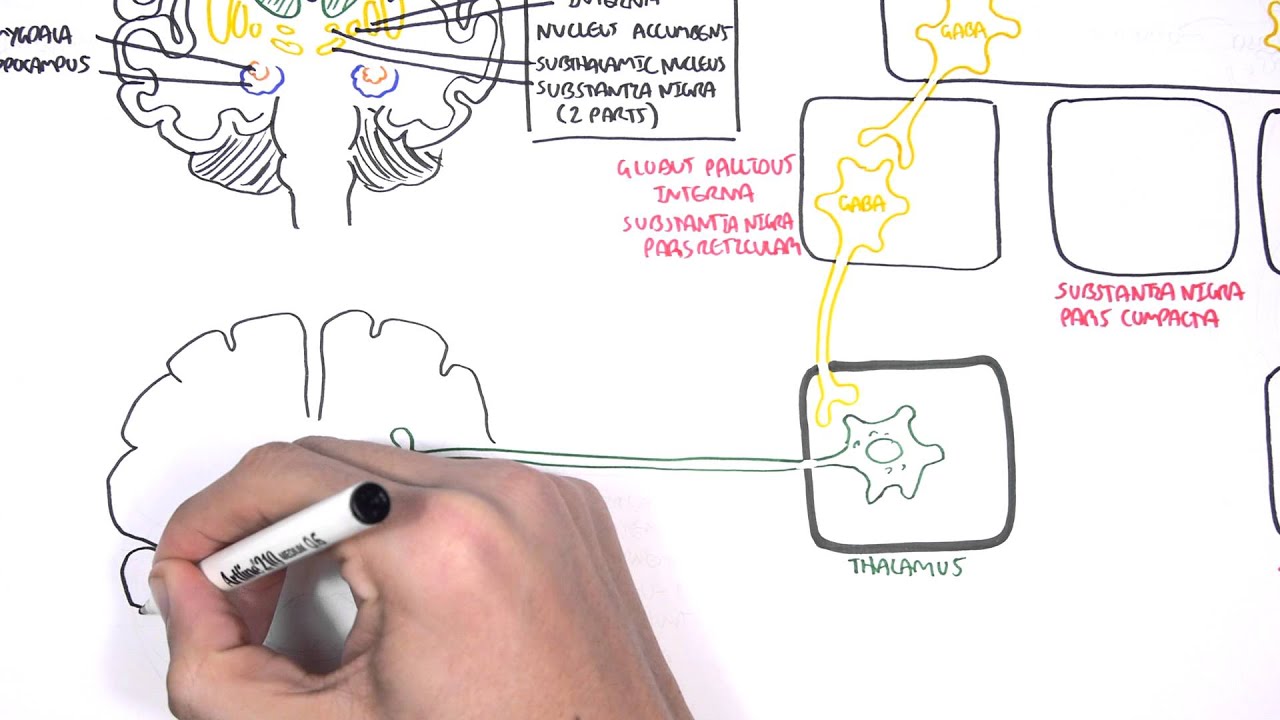
It is now well established that PD is not limited to the substantia nigrabut is instead a systemic disorder and that the neuronal protein alpha-synuclein is a major player in disease progression. Parkinsons disease PD or simply Parkinsons is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. Balestrino 2019 described Parkinsons as the second most common neurological movement disorder.
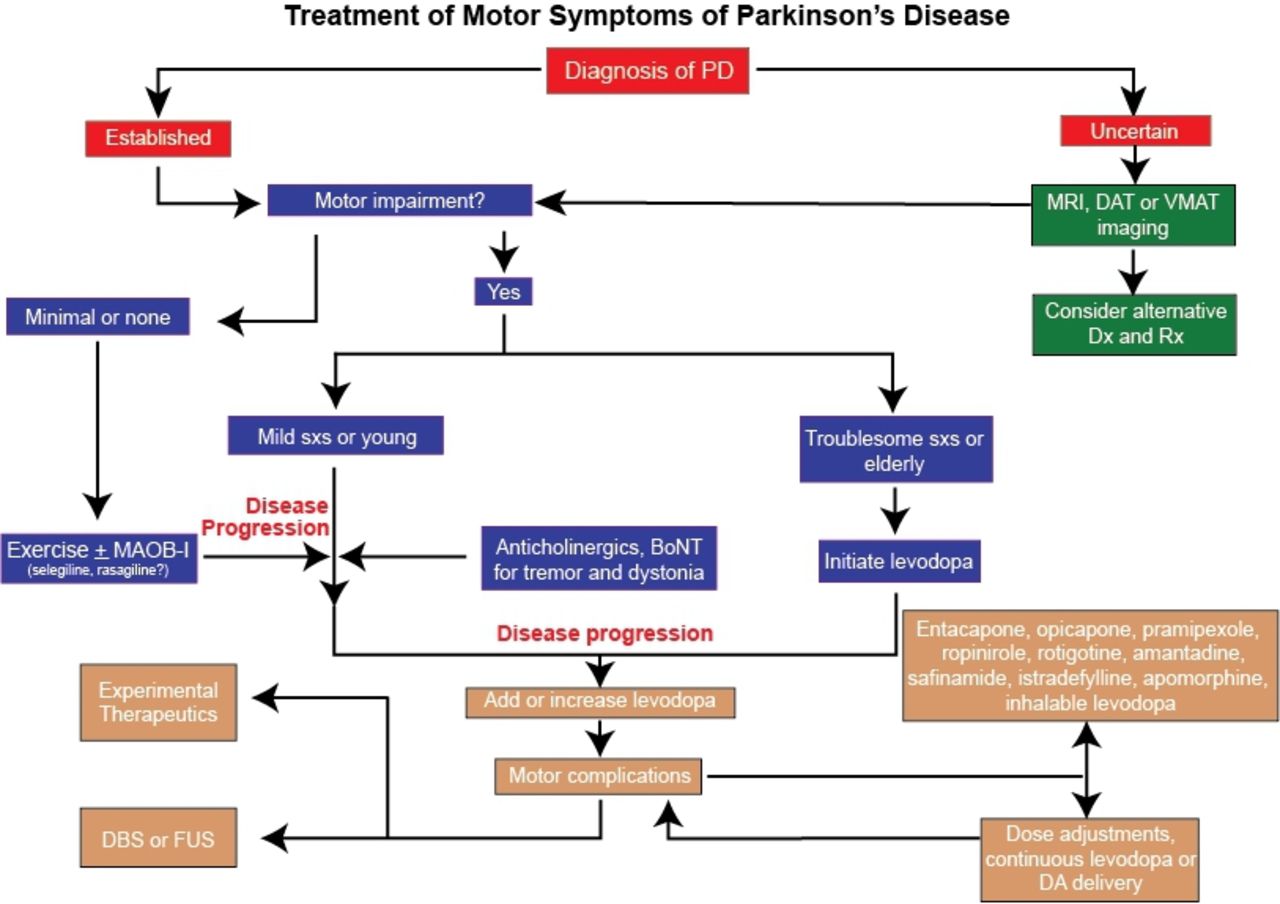
The most obvious early symptoms are tremor rigidity slowness of movement and difficulty. The motor signs of PD include hypokinetic signs such as akinesiabradykinesia rigidity and loss of normal postural reflexes and hyperkinetic signs such as tremor.
Parkinsons disease PD is characterized by motor and nonmotor cognitive and limbic deficits.
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells or neurons in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired andor die. The motor signs of PD include hypokinetic signs such as akinesiabradykinesia rigidity and loss of normal postural reflexes and hyperkinetic signs such as tremor. It affects approximately 15 to 20 of the elderly population over 60 years and 4 for those over 80 years of age. The pathophysiology is at present better understood with plurifactorial etiology including genetic predisposition and environmental toxic factors. Parkinsons disease PD or simply Parkinsons is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. However hallucinations delu-sions irritability apathy and anxiety also have been re-ported1Herewewillcommentonthemostprevalent ofthesesymptoms. Balestrino 2019 described Parkinsons as the second most common neurological movement disorder. Alpha-synuclein is an intracellular protein that is found mainly in neurological tissues but is also found in small quantities in heart muscle as well as some skeletal muscle. 1 Parkinsons Disease Jerrold Burroughs Chamberlain College of Nursing Pathophysiology Prof.
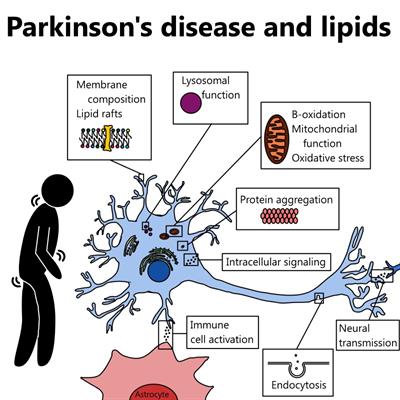
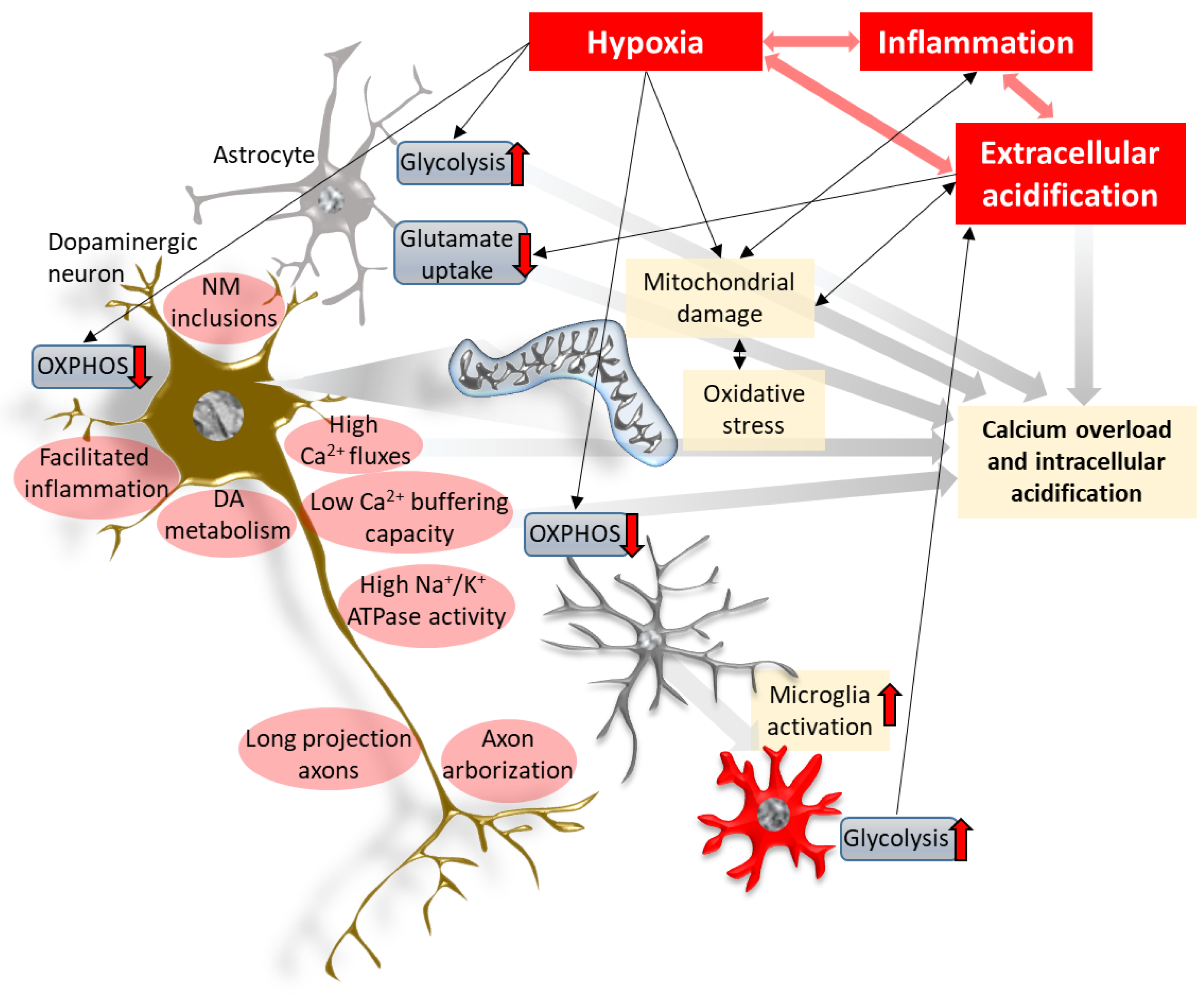
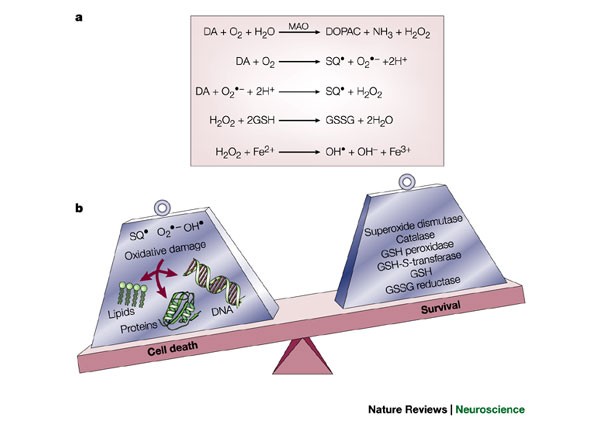
Scientists have also determined that one of the cellular mechanisms that are associated with Parkinsons disease is an accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein. This book about Parkinsons disease provides a detailed account of etiology and pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease a complicated neurological condition. 1 Parkinsons Disease Jerrold Burroughs Chamberlain College of Nursing Pathophysiology Prof. Alpha-synuclein is an intracellular protein that is found mainly in neurological tissues but is also found in small quantities in heart muscle as well as some skeletal muscle. When the neurons die or become impaired they produce less dopamine which causes the movement problems of Parkinsons. The mechanisms of cell death are based upon oxidative stress and apoptosis. Parkinsonsdiseaseappeartobeatincreasedriskforavariety ofcognitiveandpsychiatricdysfunctionsMostcommonis dementia and depression.































Post a Comment for "Pathophysiology Of Parkinson Disease"